Changes Of State In The Refrigeration Circuit
Categories: Engineering Lab EquipmentIn a compression refrigeration system a refrigerant flows through the refrigeration circuit and is subject to different changes of state. Here, the physical effect is used that during the transition o...
Product
Description
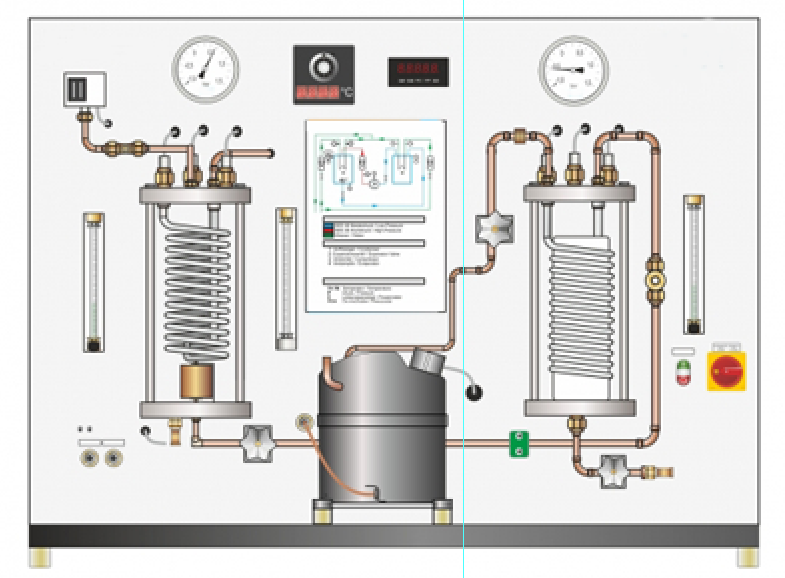
In a compression refrigeration system a refrigerant flows
through the refrigeration circuit and is subject to different changes of state.
Here, the physical effect is used that during the transition of the refrigerant
from a liquid to a gaseous state energy is required which is removed from the
environment (evaporation enthalpy). The experimental unit represents a typical
refrigeration circuit consisting of a hermetic piston compressor, condenser,
expansion valve and evaporator. The evaporator and condenser are transparent to
provide good monitoring of the phase transition process during evaporation and
condensation. The operation of the float valve as expansion valve is also easy
to observe. Before the entry into the evaporator the aggregate state of the refrigerant
can be monitored at a sight glass. A water circuit cools the condenser or
supplies the cooling load for the evaporator. Cold and hot water and
refrigerant flows are adjustable. The low pressure level of the refrigerant
used permits the use of an evaporator and condenser out of glass.
Learning Objectives/Experiments
Design and operation of a compression refrigeration system
Observe the evaporation and condensation of the refrigerant
Represent and understand the refrigeration cycle in the log
p-h diagram
Energy balances
Calculation of the coefficient of performance
Specification
Demonstration of the processes in a refrigeration circuit
For better process monitoring the evaporator and condenser
are of transparent design
Evaporator and condenser with pipe coil
Expansion valve in the shape of a float valve
Pressure switch to protect the compressor
Temperature sensor, power meter, manometer in the
refrigeration circuit, flow meter for hot and cold water and refrigerant
Safety valves at the evaporator and condenser
Refrigerant Solkatherm
Technical Data
Hermetic piston compressor
capacity: 18,3cm3
Evaporator capacity: approx. 2800mL
Condenser capacity: approx. 2800mL
Refrigerant
SES36
GWP: 4121
filling volume: 1,2kg
CO2-equivalent: 4,9t
Measuring ranges
temperature: 8x -20…200°C
pressure: 2x -1…1,5bar
flow rate:
2x 0…48L/h (water)
0…700L/h (refrigerant)
power: 0…1200W
230V, 50Hz, 1 phase
230V, 60Hz, 1 phase
120V, 60Hz, 1 phase
quick overview :
In a compression refrigeration system a refrigerant flows
through the refrigeration circuit and is subject to different changes of state.
Here, the physical effect is used that during the transition of the refrigerant
from a liquid to a gaseous state energy is required which is removed from the
environment (evaporation enthalpy). The experimental unit represents a typical
refrigeration circuit consisting of a hermetic piston compressor, condenser,
expansion valve and evaporator. The evaporator and condenser are transparent to
provide good monitoring of the phase transition process during evaporation and
condensation. The operation of the float valve as expansion valve is also easy
to observe. Before the entry into the evaporator the aggregate state of the refrigerant
can be monitored at a sight glass. A water circuit cools the condenser or
supplies the cooling load for the evaporator. Cold and hot water and
refrigerant flows are adjustable. The low pressure level of the refrigerant
used permits the use of an evaporator and condenser out of glass.
Learning Objectives/Experiments
Design and operation of a compression refrigeration system
Observe the evaporation and condensation of the refrigerant
Represent and understand the refrigeration cycle in the log
p-h diagram
Energy balances
Calculation of the coefficient of performance
Specification
Demonstration of the processes in a refrigeration circuit
For better process monitoring the evaporator and condenser
are of transparent design
Evaporator and condenser with pipe coil
Expansion valve in the shape of a float valve
Pressure switch to protect the compressor
Temperature sensor, power meter, manometer in the
refrigeration circuit, flow meter for hot and cold water and refrigerant
Safety valves at the evaporator and condenser
Refrigerant Solkatherm
Technical Data
Hermetic piston compressor
capacity: 18,3cm3
Evaporator capacity: approx. 2800mL
Condenser capacity: approx. 2800mL
Refrigerant
SES36
GWP: 4121
filling volume: 1,2kg
CO2-equivalent: 4,9t
Measuring ranges
temperature: 8x -20…200°C
pressure: 2x -1…1,5bar
flow rate:
2x 0…48L/h (water)
0…700L/h (refrigerant)
power: 0…1200W
230V, 50Hz, 1 phase
230V, 60Hz, 1 phase
120V, 60Hz, 1 phase
Product
Reviews
add Review
reviews
No Review Yet.
Copyrights © 2025 All Rights Reserved by Atico













Product
Reviews
add Review
reviews
No Review Yet.