Fundamentals of Water Flow
Categories: Engineering Lab EquipmentIn the field of fluid mechanics of incompressible fluids a distinction can be made between pipe flow and open-channel flow. With sufficient pressure and flow velocity in the completely filled pipe, th...
Product
Description
In the field of fluid mechanics of incompressible fluids a distinction can be made between pipe flow and open-channel flow. With sufficient pressure and flow velocity in the completely filled pipe, the flow is considered as one-dimensional for reasons of simplicity. Due to this precondition physical phenomena can easily be described and calculated. Open-channel flow in contrast is always multidimensional.
The compact experimental unit enables a variety of experiments on the fundamentals of incompressible flow in open channels and pipes.
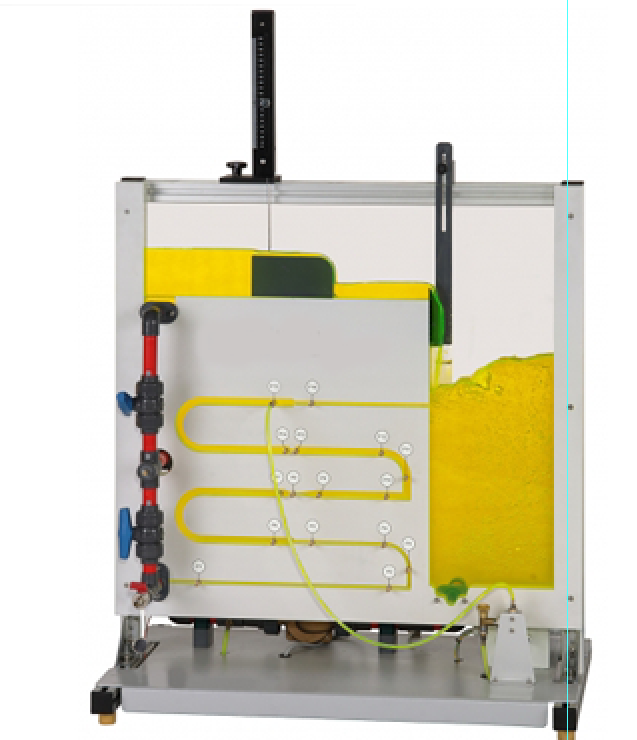
A pump supplies water from the storage tank through the supply line into the open channel or the pipe. The flow processes are clearly visible since all parts are made of transparent plastic.
In the pipe section the water flows through an orifice, a Venturi nozzle, a contraction, an enlargement as well as pipe bends and pipe angles of varying diameters. The open channel has a broad-crested weir and a sharp-crested weir. A valve is used to close off or open up the two different working sections.
Learning Objectives/Experiments
Fundamentals of pipe flow and open-channel flow
Differential pressure measurement at the orifice, Venturi nozzle, pipe bends and pipe angles, contraction and enlargement
Investigation of weir structures in an open channel
In conjunction with the power meter
Recording a pump characteristic
Specification
Investigation of the fundamentals of different areas of incompressible flow
Closed water circuit with pump
Transparent pipe section and open channel
Experiments on pressure losses at pipe bends and pipe angles, Venturi nozzle, orifice plate
One broad-crested weir and one sharp-crested weir
Horizontally travelling level gauge with vertically travelling probe tip to measure the water levels
Pressure measuring points for differential pressure measurement before and after the respective pipe resistances
Measurement of the power consumption of the pump with power meter
Technical data
Pump, 3 stages
max. power consumption: 100W
max. flow rate: 83L/min
max. head: 6m
Electronic water level gauge
measuring range: 0…200mm
graduation: 1mm
travel: max. 205mm
Measuring ranges
differential pressure: 0…600mbar
flow rate: 3,5…50L/min
230V, 50Hz, 1 phase
230V, 60Hz, 1 phase
120V, 60Hz, 1 phase
UL/CSA optional
Dimensions and weight
LxWxH: 850x540x970mm
Weight: approx. ca. 50kg
quick overview :
In the field of fluid mechanics of incompressible fluids a distinction can be made between pipe flow and open-channel flow. With sufficient pressure and flow velocity in the completely filled pipe, the flow is considered as one-dimensional for reasons of simplicity. Due to this precondition physical phenomena can easily be described and calculated. Open-channel flow in contrast is always multidimensional.
The compact experimental unit enables a variety of experiments on the fundamentals of incompressible flow in open channels and pipes.
A pump supplies water from the storage tank through the supply line into the open channel or the pipe. The flow processes are clearly visible since all parts are made of transparent plastic.
In the pipe section the water flows through an orifice, a Venturi nozzle, a contraction, an enlargement as well as pipe bends and pipe angles of varying diameters. The open channel has a broad-crested weir and a sharp-crested weir. A valve is used to close off or open up the two different working sections.
Learning Objectives/Experiments
Fundamentals of pipe flow and open-channel flow
Differential pressure measurement at the orifice, Venturi nozzle, pipe bends and pipe angles, contraction and enlargement
Investigation of weir structures in an open channel
In conjunction with the power meter
Recording a pump characteristic
Specification
Investigation of the fundamentals of different areas of incompressible flow
Closed water circuit with pump
Transparent pipe section and open channel
Experiments on pressure losses at pipe bends and pipe angles, Venturi nozzle, orifice plate
One broad-crested weir and one sharp-crested weir
Horizontally travelling level gauge with vertically travelling probe tip to measure the water levels
Pressure measuring points for differential pressure measurement before and after the respective pipe resistances
Measurement of the power consumption of the pump with power meter
Technical data
Pump, 3 stages
max. power consumption: 100W
max. flow rate: 83L/min
max. head: 6m
Electronic water level gauge
measuring range: 0…200mm
graduation: 1mm
travel: max. 205mm
Measuring ranges
differential pressure: 0…600mbar
flow rate: 3,5…50L/min
230V, 50Hz, 1 phase
230V, 60Hz, 1 phase
120V, 60Hz, 1 phase
UL/CSA optional
Dimensions and weight
LxWxH: 850x540x970mm
Weight: approx. ca. 50kg
Product
Reviews
add Review
reviews
No Review Yet.
Copyrights © 2025 All Rights Reserved by Atico













Product
Reviews
add Review
reviews
No Review Yet.