Introduction To Refrigeration
Categories: Engineering Lab EquipmentWith simple and clear experiments this equipment is intended mainly as a basic introduction to refrigeration. It enables familiarisation with the operation and handling of a refrigeration system. The...
Product
Description
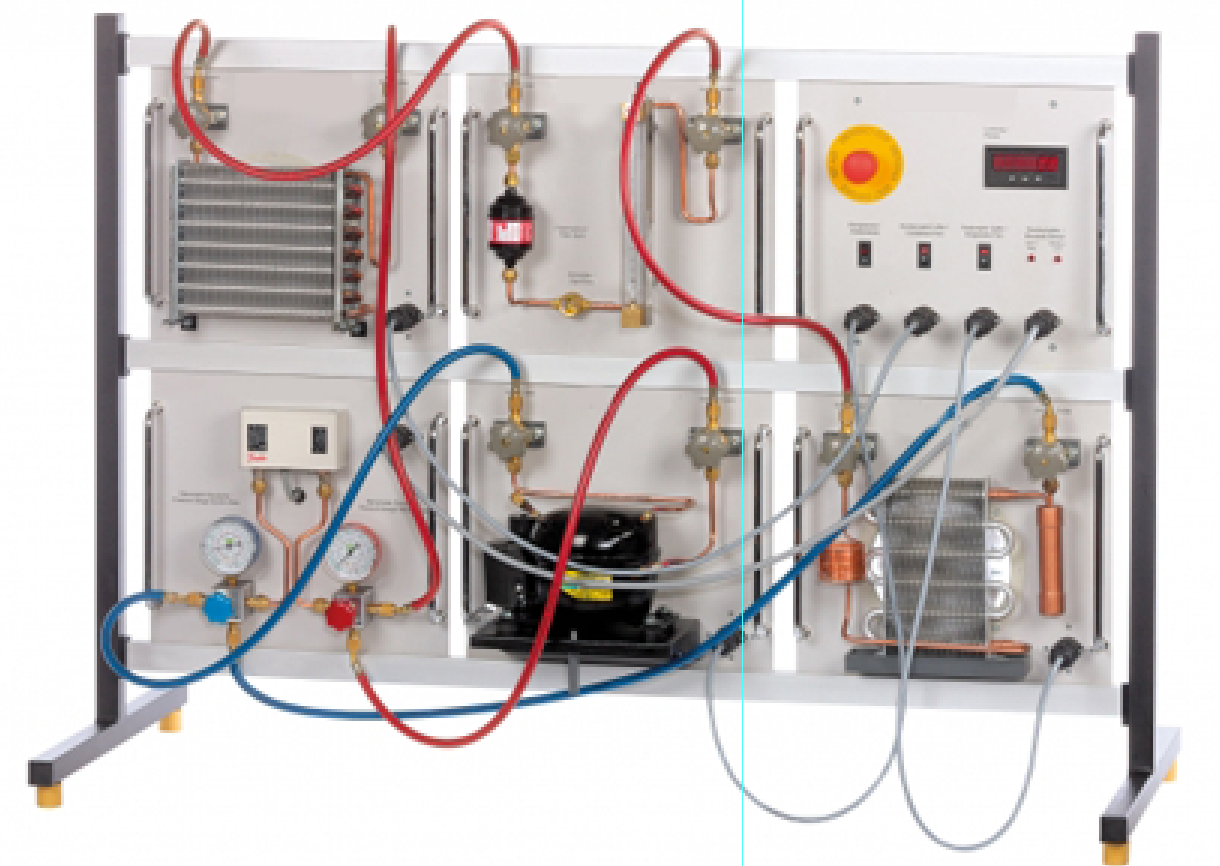
With simple and clear experiments this equipment is intended
mainly as a basic introduction to refrigeration. It enables familiarisation
with the operation and handling of a refrigeration system. The experimental
unit includes all the necessary components for a fully operational
refrigeration circuit, such as compressor, condenser, evaporator and a
capillary tube as expansion element. Other components complement the scope of
the equipment: display and control panel, pressure switches and pressure display
to protect the compressor against excessive pressure and a flow meter and sight
glass with filter/drier. Condenser and evaporator are each present twice: as
air/refrigerant heat exchanger and as water/refrigerant heat exchanger. This
allows for different component combinations. The components are mounted on
plates and form installation-ready modules. 6 of the 8 modules are positioned
in the frame at any one time and connected via hoses and supply cables. This
allows for the construction of different simple compression refrigeration
systems. For filling the system the refrigerant filling and evacuation
equipment is recommended.
Learning Objectives/Experiments
Fundamentals of a simple refrigeration circuit
Detection and understanding of the cyclic process
Changes of state of the refrigerant
Representation the refrigeration circuit in the process
schematic
Representation of the cyclic process in the log p-h diagram
Estimating key figures, refrigeration capacity and heat
fluxes
Different operating modes
Air cooling
Generating cold water
Heat pump (generate hot water)
Practical exercises
Draining and filling the refrigeration system
Fault finding
Specification
Setup of simple refrigeration circuits with different
components
8 self-contained operational modules mounted on a plate each
Light-weight aluminium frame to arrange 6 modules
Evaporator and condenser each available as air/refrigerant
heat exchanger (finned tube heat exchanger) and as water/refrigerant heat
exchanger (with pipe coil)
Modules fitted with manual valves
Components connected via hoses
Technical Data
Hermetic refrigerant compressor
power consumption: 67W at 5/40°C
refrigeration capacity: 152W at 5/40°C
Tank content
water tank, evaporator: 2L
water tank, condenser: 3L
Pressure switch activation pressure
LP: 1bar
HP: 14bar
Manometer
inlet side (low pressure): 1…10bar
outlet side (high pressure): 1…30bar
Rotameter: 0…7,4L/h
Refrigerant
R513A
GWP: 631
filling volume: 400g
CO2-equivalent: 0,3t
230V, 50Hz, 1 phase
230V, 60Hz, 1 phase
120V, 60Hz, 1 phase
quick overview :
With simple and clear experiments this equipment is intended
mainly as a basic introduction to refrigeration. It enables familiarisation
with the operation and handling of a refrigeration system. The experimental
unit includes all the necessary components for a fully operational
refrigeration circuit, such as compressor, condenser, evaporator and a
capillary tube as expansion element. Other components complement the scope of
the equipment: display and control panel, pressure switches and pressure display
to protect the compressor against excessive pressure and a flow meter and sight
glass with filter/drier. Condenser and evaporator are each present twice: as
air/refrigerant heat exchanger and as water/refrigerant heat exchanger. This
allows for different component combinations. The components are mounted on
plates and form installation-ready modules. 6 of the 8 modules are positioned
in the frame at any one time and connected via hoses and supply cables. This
allows for the construction of different simple compression refrigeration
systems. For filling the system the refrigerant filling and evacuation
equipment is recommended.
Learning Objectives/Experiments
Fundamentals of a simple refrigeration circuit
Detection and understanding of the cyclic process
Changes of state of the refrigerant
Representation the refrigeration circuit in the process
schematic
Representation of the cyclic process in the log p-h diagram
Estimating key figures, refrigeration capacity and heat
fluxes
Different operating modes
Air cooling
Generating cold water
Heat pump (generate hot water)
Practical exercises
Draining and filling the refrigeration system
Fault finding
Specification
Setup of simple refrigeration circuits with different
components
8 self-contained operational modules mounted on a plate each
Light-weight aluminium frame to arrange 6 modules
Evaporator and condenser each available as air/refrigerant
heat exchanger (finned tube heat exchanger) and as water/refrigerant heat
exchanger (with pipe coil)
Modules fitted with manual valves
Components connected via hoses
Technical Data
Hermetic refrigerant compressor
power consumption: 67W at 5/40°C
refrigeration capacity: 152W at 5/40°C
Tank content
water tank, evaporator: 2L
water tank, condenser: 3L
Pressure switch activation pressure
LP: 1bar
HP: 14bar
Manometer
inlet side (low pressure): 1…10bar
outlet side (high pressure): 1…30bar
Rotameter: 0…7,4L/h
Refrigerant
R513A
GWP: 631
filling volume: 400g
CO2-equivalent: 0,3t
230V, 50Hz, 1 phase
230V, 60Hz, 1 phase
120V, 60Hz, 1 phase
Product
Reviews
add Review
reviews
No Review Yet.
Copyrights © 2025 All Rights Reserved by Atico













Product
Reviews
add Review
reviews
No Review Yet.