- Admin
- 0 Comments
1. Basic Laboratory Equipment
a. Glassware
Beakers: For mixing and heating liquids.
Flasks: Including volumetric flasks for precise measurements.
Test Tubes: For conducting small-scale reactions.
Pipettes: For accurate liquid transfers.
b. Measuring Instruments
Balances: Analytical and top-loading balances for precise weight measurements.
Graduated Cylinders: For measuring volumes accurately.
Thermometers: Digital or mercury for temperature measurements.
c. Consumables
Petri Dishes: For culturing microorganisms.
Microcentrifuge Tubes: Essential for molecular biology experiments.
Filter Paper: For filtration processes.
2. Safety Equipment
a. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Lab Coats: To protect clothing and skin.
Gloves: Nitrile or latex gloves for chemical handling.
Safety Goggles: Protect eyes from splashes and harmful substances.
b. Safety Gear
Fume Hoods: Essential for handling volatile substances safely.
Eyewash Stations: For immediate rinsing in case of chemical exposure.
Fire Extinguishers: Required for emergency fire situations.
3. Heating and Cooling Equipment
a. Heating Devices
Bunsen Burners: For flame-based heating applications.
Hot Plates: For uniform heating of samples.
Ovens: For drying or sterilization processes.
b. Cooling Equipment
Refrigerators: For storing temperature-sensitive samples.
Cryogenic Freezers: For long-term storage of biological samples.
4. Analytical Instruments
a. Spectroscopy
UV-Vis Spectrophotometers: For measuring absorbance and concentration.
Infrared Spectrometers: For molecular analysis.
b. Chromatography
HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography): For separating compounds.
GC (Gas Chromatography): For analyzing volatile substances.
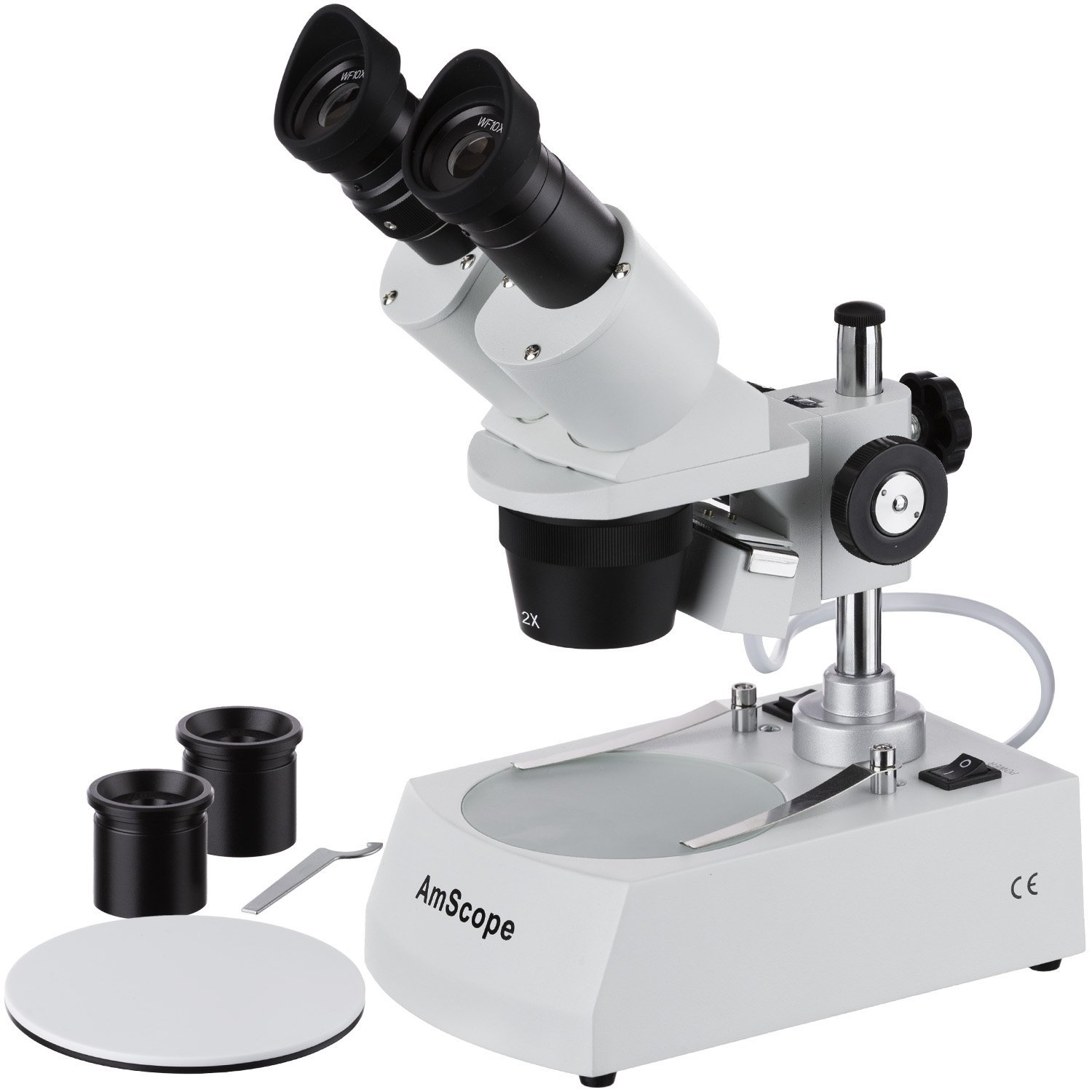
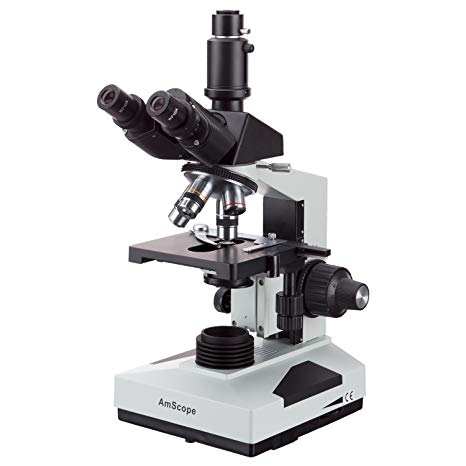
c. Microscopy
Light Microscopes: For observing small specimens.
Electron Microscopes: For high-resolution imaging at the nanoscale.
5. Biological and Chemical Analysis Equipment
a. Centrifuges
Essential for separating components in liquids based on density.
b. Incubators
For maintaining optimal conditions for cell cultures and biological samples.
c. PCR Machines
Critical for molecular biology applications, especially in DNA amplification.
6. Electrical and Electronic Equipment
a. Power Supplies
For powering various lab instruments and experiments.
b. Data Logging Systems
For monitoring and recording experimental data over time.
c. Multimeters
For electrical measurements, ensuring equipment functionality.
7. Specialized Equipment
a. Reagents and Chemical Storage
Chemical Cabinets: For safe storage of hazardous materials.
Refrigerated Storage Units: For temperature-sensitive chemicals.
b. Biosafety Cabinets
For safe handling of infectious materials or hazardous biological agents.
c. Autoclaves
For sterilizing lab equipment and materials.
8. Furniture and Lab Setup
a. Lab Benches and Tables
Durable and chemical-resistant surfaces for conducting experiments.
b. Storage Solutions
Cabinets and shelves for organized storage of materials and equipment.
c. Sink and Waste Disposal Units
For managing spills and waste safely.
9. Supplier Considerations in Delhi
When sourcing lab equipment, it